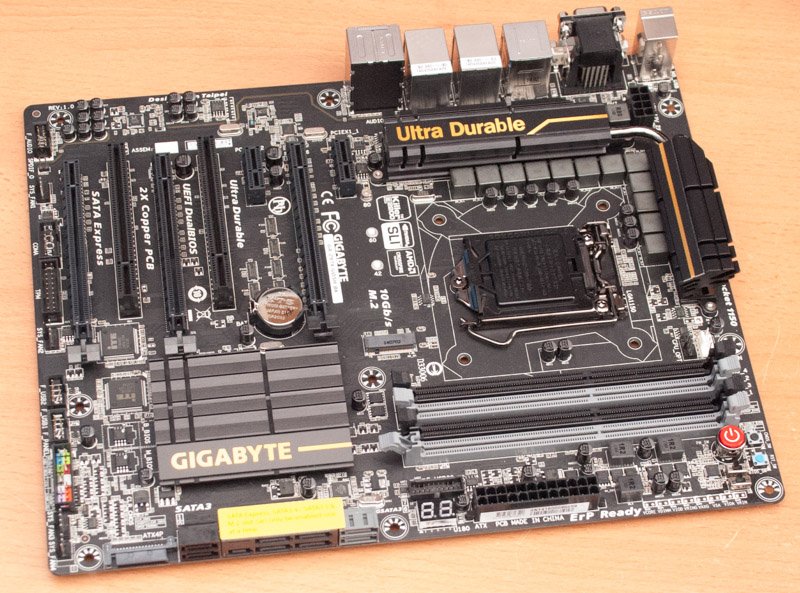
To increase the longevity of your computer, you need to be familiar with the anatomy of a motherboard. If you have never taken apart a PC before, it may look like a pile of tangled wires and random chips. Learning about how it works can be overwhelming when you are in this situation.
The purpose of this article is to help you understand where all the components on your motherboard go and what they do.
What is a Motherboard?
Your motherboard is the permanent base for all of your computer components. The motherboard is a printed circuit board that houses your processor and multiple sockets for expansion cards.
It is a series of different components that all work together to bring your computer to life. A motherboard functions as a bridge between the software you use and the computer hardware that lets it run. Every motherboard has a bunch of individual components, each doing specific jobs to make sure that the whole thing works correctly.
They contain the CPU, which performs calculations, and the RAM, where the OS, software, and files are stored. The motherboard also contains other components necessary for operating a PC, including network cards, USB, and more.
Different Components of a Motherboard
Let’s understand the different components that make up a motherboard.
1. CPU Chip
The function of a CPU chip is to handle the computational needs and calculations of the computer. This means it must do the math of inputs and outputs, controlling all that happens with how the information flows through a computer.
2. RAM (Random Access Memory) slots
This computer memory can be read and written and is used to save data and machine code. Memory is the most important component on the motherboard, and you should consider it before making your choice. The memory capacity of your motherboard depends on how powerful you want to make your computer hardware.
3. ROM Chip
ROM stands for “Read-Only Memory.” It is a type of memory chip that is non-volatile. It does not require any power to access the information stored on it.
Simply put, the content stored in ROM will not be erased even after you cut off power. The BIOS info is stored in ROM.
4. USB (Universal serial bus)
It is a multi-purpose connection for PCs. USB devices have features like hot-swap. You don’t have to restart your system to insert or remove them.
5. Southbridge/northbridge
The southbridge is an IC chip on the motherboard that runs and controls IO functionality.
The northbridge is also called Host Bridge or Memory Controller Hub. It is the main controller that directs traffic to and from the CPU.
The northbridge and the southbridge together manage communications between the CPU and different motherboard components.
6. PCI Slots and PCI Chip
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) lets you connect different hardware components such as disk controllers, modems, NIC cards, graphics cards, and additional USB without the need to add or replace your motherboard.
7. AGP Slot and Chip
AGP Slot (Accelerated Graphics Port Slot) is a brown expansion slot frequently used for graphics cards.
8. The CMOS Battery
In motherboards, there is a small separate memory block made from CMOS RAM chips. It is kept alive by a CMOS battery even when you cut off PC power. This stops reconfiguration when you switch on your PC.
9. The Computer Cache Memory
It is a small high-speed memory block (RAM) that improves PC performance that preloads info from the (comparatively slow) main memory and passes it to the processor whenever required.
In most CPUs, you will find an in-built internal cache memory, known as Level 1 or primary cache memory. This can be enhanced by an external Level 2 or secondary cache memory which is fitted on the motherboard.
Modern computers have Levels 1 and 2 cache memory built into the processor die. In case you implement a third external cache, you can call it the Level 3 (L3) cache.
10. The Expansion Buses
It is an input and output path from the CPU to secondary devices, consisting of a series of slots. You plug in the expansion boards into the bus.
Expansion buses improve your PC’s capabilities as you can add missing features to your PC by slotting adapter cards.
11. Power Supply Plug
Motherboards have some essential components that make them work. One of the most crucial is the power supply plug which delivers power to different components in the motherboard. It supplies power to the motherboard as well as its connected components and peripherals.
12. SATA and PATA Port and Connector
PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment) is a ribbon cable. It has 40 pins that connect mass storage devices, including hard disks and optical drives to your PC.
Each PATA cable comes with two or three connectors. One connector is linked to the adapter interfacing, while the rest are connected to secondary storage devices.
In modern computers, SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) has replaced PATA. SATA is a 7-pin cable. It is not only shorter but more powerful than PATA while serving the same purpose.
That’s a Wrap
Now that you know the basics of what a motherboard is, you might be wondering why you need to learn about it.
The main reason for learning about any hardware, such as your motherboard, is so that you can make informed decisions regarding future hardware purchases or upgrades.
What’s more, understanding your motherboard is key to understanding any computer system. If you want your computer to run as efficiently and effectively as possible, you need to know how all of the components on your motherboard work together. You also want to know what they do individually and why they’re there.